Vorteile von Hyprostatik
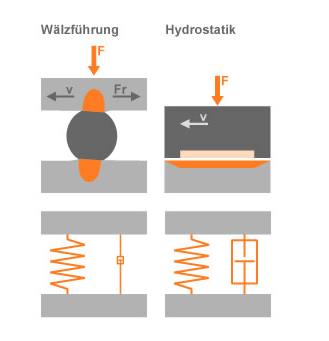
Vorteile gegenüber Walz- und Gleitsystemen
-
Zehnerpotenzen bessere Dämpfung
-
Verschleißfrei
-
Geringere Rundlauffehler und höhere Präzision von Führungen
-
Sehr geringe und geschwindigkeitsproportionale Reibung der Führungen
- Keine Kraft- und Momentstöße durch Rollenumlenkungen in Führungen und Gewindetrieben
- Geringere Verschmutzungsempfindlichkeit
- Durch die Hydrostatik größtenteils Ausgleich von Formfehlern der Führungsflächen
- Reduzierung Einbauraum durch Entfall der Wälzlagerteile
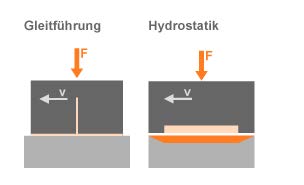
Vorteile gegenüber Gleitsystemen
-
Zehnerpotenzen bessere Dämpfung
-
Verschleißfrei
-
Geschwindigkeits- bzw. drehzahlunabhängige Eigenschaften
-
Sehr geringe Reibung von schnell laufenden Lagerungen
- Bessere Abführung der in schnell laufenden Lagerungen
entstehenden Reibungswärme aus der Maschine - Geringere Verschmutzungsempfindlichkeit
- Durch die Hydrostatik größtenteils Ausgleich von Formfehlern der Führungsflächen
Vorteile gegenüber anderen hydrostatischen Systemen
HYPROSTATIK setzt für seine Vorteile gegenüber anderen hydrostatischen Systemen den Progressiv-Mengenregler, kurz PM-Regler, ein. Dieser versorgt die hydrostatischen Taschen mit Öl. Die PM-Regler werden in Reihen- und Anbauregler unterschieden. (Verlinkung zu Produkt Reihen-PM-Regler und Anbauregler). Der PM-Regler misst am Ausgang rein mechanisch den Versorgungsdruck und regelt den Durchfluss so, dass der Spalt in den hydrostatischen Taschen konstant bleibt. Es ergeben sich dadurch signifikante Vorteile im Vergleich zu anderen hydrostatischen Systemen, wie Kapillaren, hydraulischen Blenden, Mehrkreispumpen und Laufspaltdrosseln.
-
4-5 fache Steife bei vergleichbaren Daten
-
Deutlich reduzierter Ölbedarf
-
Niedrigerer notwendiger Pumpendruck durch hohen Ausnutzungsgrad
-
Deutlich kleinere Pumpen- und Motorleistung
- Kostenvorteile
